Infrastructure
Infrastructure
- Read the definition of the term Infrastructure.
Infrastructure is the different things in a place that help that place carry out activities that make money. - Working with one or two others make a list of all the things that you can think of that make up the infrastructure of where you live.
- As a class; share your answer into a mind map type of diagram.
One thing that all leaders in Britain and Wales can agree on is the need to improve infrastructure.
In this edition of GitN we will look at the different infrastructure projects going on in the UK.
In the next edition we will look at how the Welsh Government is spending money on infrastructure to help our economy grow.
From previous editions of GitN you will know that the ‘economy’ is all about money or, more precisely, the activities which make money in a country such as Wales.
In London the UK Prime Minister decided to increase spending on infrastructure projects in 2016.
This was laid out in the government's Infrastructure Plan.
Crossrail
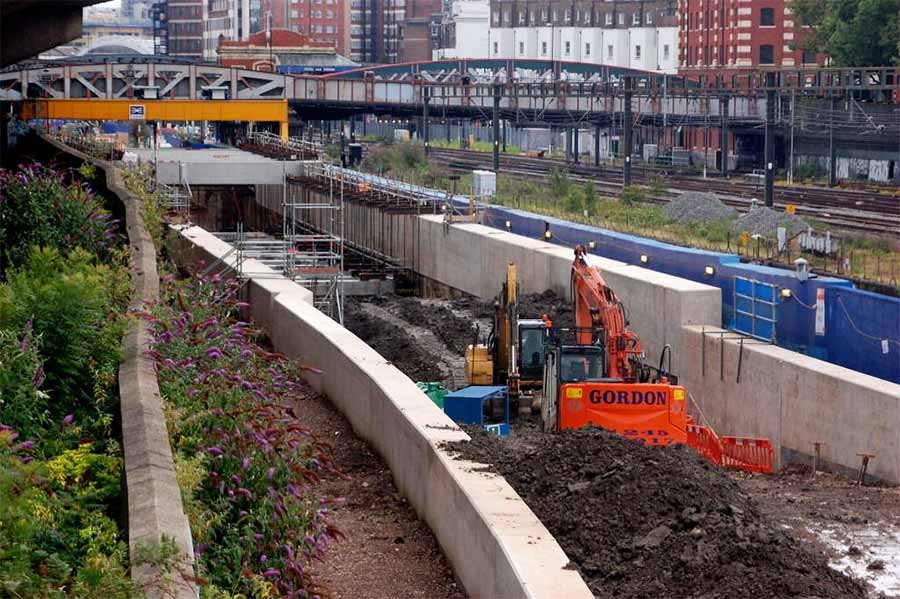

Image: Crossrail Tunnel Royal Oak Portal Construction - Marcus Rowland © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
Crossrail is a new 118 km rail route to cross London from East to West.
It will be an important link for Wales as it will improve the movement of passengers arriving from South Wales.
It will also link up with Heathrow Airport.
It will also join up with the new HS2 (HS = High Speed) rail network.
- Estimated cost - £15.9 billion.
Crossrail 2

Image: Euston Station London - geograph.org.uk - 1309275 - Richard Rogerson © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic
Crossrail 2 is a second phase of the Crossrail project.
It will link in Southern England to Crossrail and the new HS2 network at Euston Station.
- Estimated cost - £32 billion.
The National Infrastructure Delivery Plan
The plan is for the government to invest billions of pounds in infrastructure by 2020-21. This is public sector money.
Public sector spending will be partnered with even more spending by independent businesses and even individuals. This is called the private sector.
In total the plan shows how over £425 billion will be spent on over 600 projects and programmes across the UK.
There is also a further £58 billion of public (public sector) investment will be spent on social infrastructure; for housing and regeneration, education, health and justice.
The Welsh Government will also take part in this huge amount of spending on infrastructure.
Extra money will also be given to the Welsh Government to spend on the infrastructure projects decided on in Wales by the Welsh people.The Welsh Government could benefit directly with projects being paid for by London such as rail electrification in South Wales or the construction of a ‘super-prison’ in North Wales.
Some infrastructure projects are so important to Wales that the Welsh Government want new powers to be able to borrow money to spend even more on them.
High Speed Rail Network
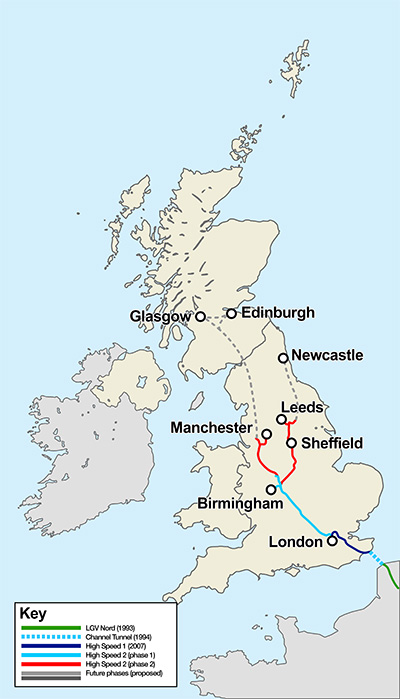
Image: UK high speed rail map - Cnbrb © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
High Speed Rail Network
HS1 – Dark Blue
HS2 (phase 1) – Light Blue
HS2 (phase 2) – Red
- Estimated cost –
- HS1 - £5.4 billion
- HS2 - £30 billion
Why is infrastructure so important?
- Think of our economy (how we make all of our money) as a cake.
- The infrastructure is the ingredients.
- The more ingredients you have, the bigger the cake.
- If certain ingredients are missing, then the cake will not be as good as it could be.
- By spending more on infrastructure, the different governments of the united Kingdom and the Devolved Nations are hoping for a bigger economy.
- To put it another way, they are wanting to spend more money to make more money.
- The HS2 rail network will cost an estimated £30 billion; over the next £30 years it will create an estimated £43 billion and £27 billion in fares.
Rail Electrification

Image: Hitachi Super Express mockup (1) - Hitachi Rail Europe © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
Great Western Line (Paddington to Swansea) Electrification.
- Cost - £5 billion
When we look at infrastructure, we usually look at it as:
Student Activity
Use a map from your local area (this could be from a GIS source such as Google Earth (Satellite view)).
Make a list of the different types of infrastructure that you can see.
Come back to your list after you have read the two linked articles, and add any important ones that you have missed out.
After each one, put a (H) for Hard or a (S) for Soft to show which ones are Hard Infrastructure and which ones are Soft Infrastructure.
After reading all three articles and carrying out the activities, use the accompanying A3 sheet to help you start a DME into infrastructure projects.
Teacher Box
The resource is designed to be used as a whole class resource from the front of the classroom on the projector/interactive whiteboard. The various graphics should be supported by teacher exposition based on the text (which will not be readable in permitted time to the vast majority of pupils), following this it is ideal that the students have access to the online resource in order to work on the activity sheet (designed to be printed on A3 size paper). Ideally these activities will be supported by the use of a network room, tablets/laptops or students' own phones/devices if permitted. However the activities are also designed to be used in a typical one hour lesson with the teacher input using the resource from the front of the classroom alongside the resource sheet. Students can then be set a homework task to study the three articles in advance of the following lesson.
The resource and accompanying sheet is designed to support the LNF framework while giving students key geographical knowledge about places in relation to infrastructure.
Pupil Box
Either in class or at home read and complete the activities in the online resource article and in the linked articles in this edition of Geography in the News. Attempt to complete all of the activities in the resource sheet.
What you will learn:
- You will increase your knowledge about the infrastructure.
- You will increase your understanding of how these factors may affect human beings and human activities
- You will have you the opportunity to learn or practice important literacy and numeracy skills.
- You will learn new geographical terms highlighted in purple. These should be learned and added to a glossary. A glossary is a list of words and their meanings. You could have one in the back of your geography exercise book. If you have a planner it is probably a good place to keep a glossary, or you may keep a separate glossary or word book. A good glossary helps you build your vocabulary and your literacy. Research meanings using related article content, discussion or a dictionary (either online or a book).

