Hard Infrastructure
Hard Infrastructure
Hard infrastructure refers to large networks constructed over large periods of time which enable a modern country or region to work. Major networks such as transport and energy supply are easy to see but there are also all of the vehicles, people and even IT/software which are required to enable these to work. Added to this are the homes for people to live and the services essential for both individuals and businesses to thrive including waste management, water supply, flood prevention and communications.
Transportation
- Road networks
- Structures like bridges
- Signs/markings
- Electrical
- Street lighting
- Traffic signals
- Fuel supply
- Service areas

ROAD NETWORKS BECOME MORE COMPLEX (ISSUE 8)
- Public Transport Systems
- Rail systems
- Underground
- Overground
- Bus networks
- Tram networks
- Bicycle networks
- Pedestrian pavements and safe crossings
- Rail systems

TRAINS ARE A TRUE ALTERNATIVE TO THE CAR (ISSUE 8)
- Airports and air transport
- Seaports, ferries and seaways

INCREASINGLY LARGE CRUISE SHIPS ARE VISITING WALES (ISSUE 15)
- Canals and navigable waterways
Housing
- Houses / flats to buy
- Houses / flats to rent

ELECTRICITY GENERATION AT HOME (ISSUE 12)
Energy
- Electrical power network
- Generation plants
- Non-Renewable
- Renewable
- Electrical grid
- Substations
- Local distribution
- Generation plants

FOSSIL FUELS AT HOME AND ON THE MOVE (ISSUE 15)
- Natural gas network
- Production sites
- Refinement
- Transport
- Pipeline
- Ship
- Road
- Bottled
- Storage and distribution terminals
- Local distribution network

LNG GAS TANKER MILFORD HAVEN IN WEST WALES. Image: Methanier aspher LNGRIVERS - Pline © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
- Petroleum
- Production sites – oil wells
- Refinement
- Transport
- Pipeline
- Ship
- Road
- Storage
- Local distribution network
- Coal
- Mining
- Washing
- Transportation

COAL MINING HISTORY OF WALES (ISSUE 7)
Water Management
- Drinking water supply
- Storage reservoirs
- Pumps
- Filtration and treatment
- Distribution pipelines

SAVE US FROM OUR SEWAGE (SEE ISSUE 23)
- Sewage
- Collection sewers
- Water Treatment Centres
- Waste water disposal

FLOODING (SEE ISSUE 3 & 32)
- Drainage systems
- Storm drains/drain networks
- Ditches and channels
- Irrigation systems
- Reservoirs
- Pumps
- Irrigation canals
- Flood control systems
- Flood walls/raised banks
- Pumping stations
- Floodgates
- Storage reservoirs
- Coastal management
- Seawalls
- Breakwaters
- Groynes
- Beach nourishment
- Sand dune stabilisation

SEA DEFENCES AT ABERAVON (ISSUE 18)
Communications
- Postal service
- Postage boxes
- Sorting facilities
- Delivery service
- Telephone networks
- Landlines
- Exchange systems
- Mobile phone networks
- Masts
- Exchanges
- Internet Services
- Telephone copper land lines
- Fibre optic cables
- Mobile
- Servers

SEE ISSUE 8 TO FIND OUT ABOUT AREAS OF WALES WITHOUT ACCESS TO FAST BROADBAND SERVICES
- Television/radio
- Ground transmission
- Satellite transmission
- Cable networks
- Regulations and standards
- Communications satellites
- Undersea cables
Solid waste management
- Household waste collection
- Recyclables collection
- Landfill waste

RECYCLING WASTE IN WALES (ISSUE 7)
- Solid waste incinerators
- Heat production
- Electricity production
- Materials recovery facilities (recycling)
- Landfill
- Hazardous waste disposal facilities
Plans for City Regions
It is proposed that Wales will benefit from two proposed city regions. North-East Wales will benefit from the proposed Northern Powerhouse; a city region with its hub in Manchester stretching to the West to Liverpool (and North-East Wales) and Eastwards to Leeds and Newcastle.
NEW £212 MILLION PRISON BEING BUILT NEAR WREXHAM
The idea behind the Northern Powerhouse is to balance the economy by bringing more jobs to the northern half of Britain. North Wales will benefit from improved rail and road networks (see issue 8); increased job opportunities, and increased house building. Already projects such as a new 'Super Prison' are being built near Wrexham and new energy projects are planned or are already being built (see issues 12 & 13).
In South Wales a city region has been proposed made up of 10 current Local Authority areas. The region would be based around the capital city in Cardiff and help to link the South Wales Valleys and the Newport/Cwmbran urban area. Public transport will be improved with the construction of a new network of buses, trains, trams & light rail transport in what has been termed as the South Wales Metro.
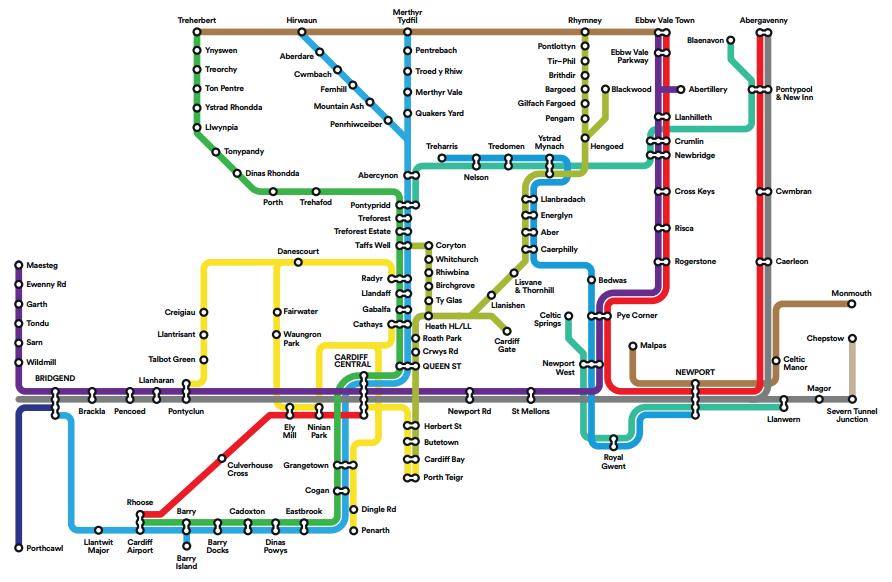 Image: SW Metro - Welsh Government © Crown copyright 2016 under the Open Government Licence v3.0
Image: SW Metro - Welsh Government © Crown copyright 2016 under the Open Government Licence v3.0
The Cardiff City Region plan will cost £1.2 billion of public money. Already there is a £5 billion upgrade underway of the main railway from Swansea to London Paddington. The Welsh Government has bought Cardiff Airport which will be upgraded. A consultation is also underway on a £1 billion (plus) programme to build a motorway bypass around Newport which currently experiences large traffic jams every day at a 'bottleneck' where the motorway changes from 8 lanes (including the hard shoulder) to 4 lanes to pass through tunnels through a local hill.
Use a GIS (Geographical Information System) such as Google Earth (satellite view would be good) to get a map of an urban area (towns and cities) and an equal sized map of a rural area (countryside) that you know personally.
1) Draw up a table to list the different examples of hard infrastructure found on each map. Try to find at least 12 in the urban area and at least 5 in the rural area.
| Hard Infrastructure | |||
| Urban Area | Rural Area | ||
| 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 2 | ||
| 3 | 3 | ||
| 4 | 4 | ||
| 5 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 6 | ||
| 7 | 7 | ||
| 8 | 8 | ||
| 9 | 9 | ||
| 10 | 10 | ||
| 11 | 11 | ||
| 12 | 12 | ||
2) What was easier; to find 12 in an urban area or 5 in a rural area?

