What Are The Main Sources Of Migrants For the EU at Present?
Describe the location of the regions marked 1-4
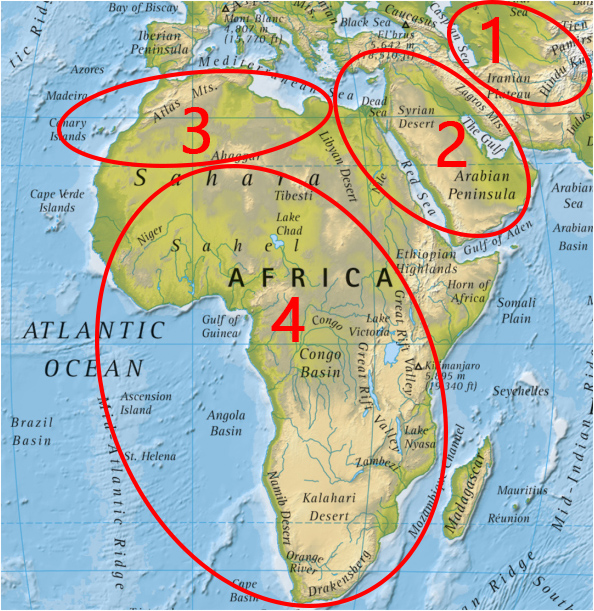
Look at the map – Describe locations 1-4.
Clue
- North Africa
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Afghanistan (and Neighbours)
- The Middle East
Answers
- Afghanistan (and Neighbours)
- The Middle East
- North Africa
- Sub-Saharan Africa
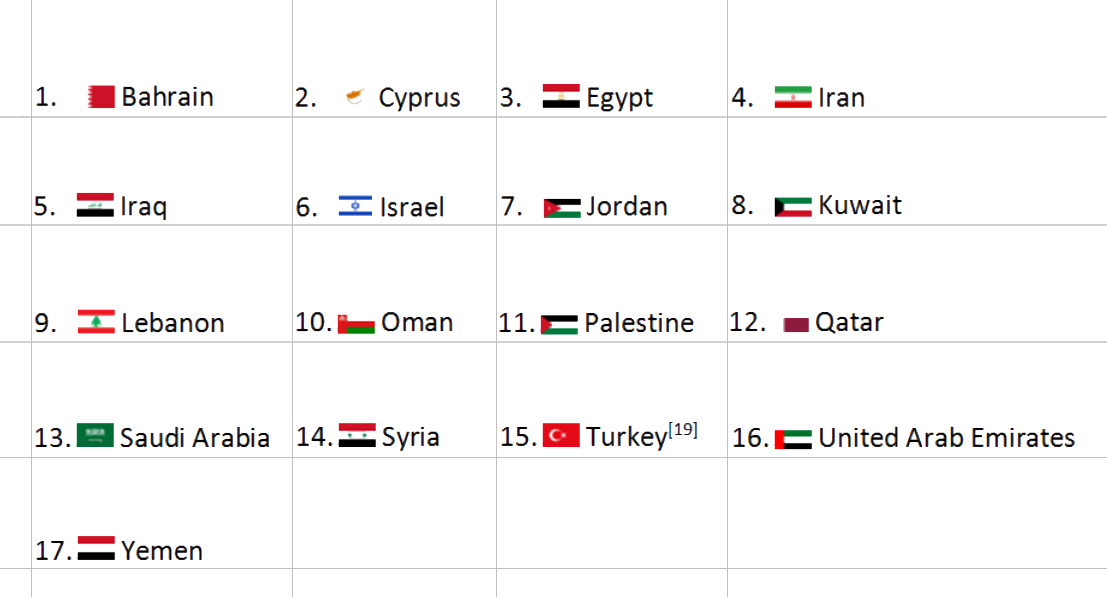
Look at the map of THE Middle East. Use the list below to name the countries numbered 1-17.
Use group discussion and an atlas or online digital atlas to do this.
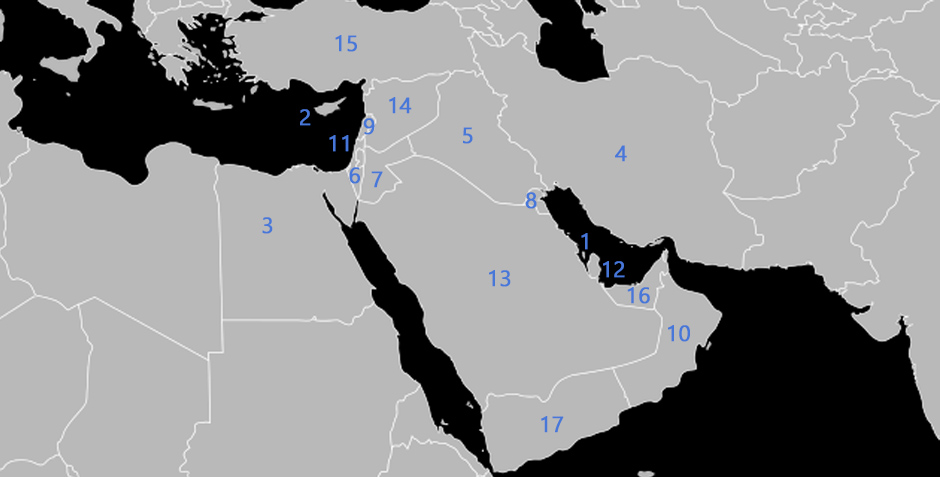
Image: Middle East - Madhero88 © Wikimedia Commons
Investigating Migration
We are going to investigate the countries where many are leaving to go to safer places such as Europe.
These are:
- The Middle East
- Iraq
- Syria
- Africa
- North Africa
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Afghanistan
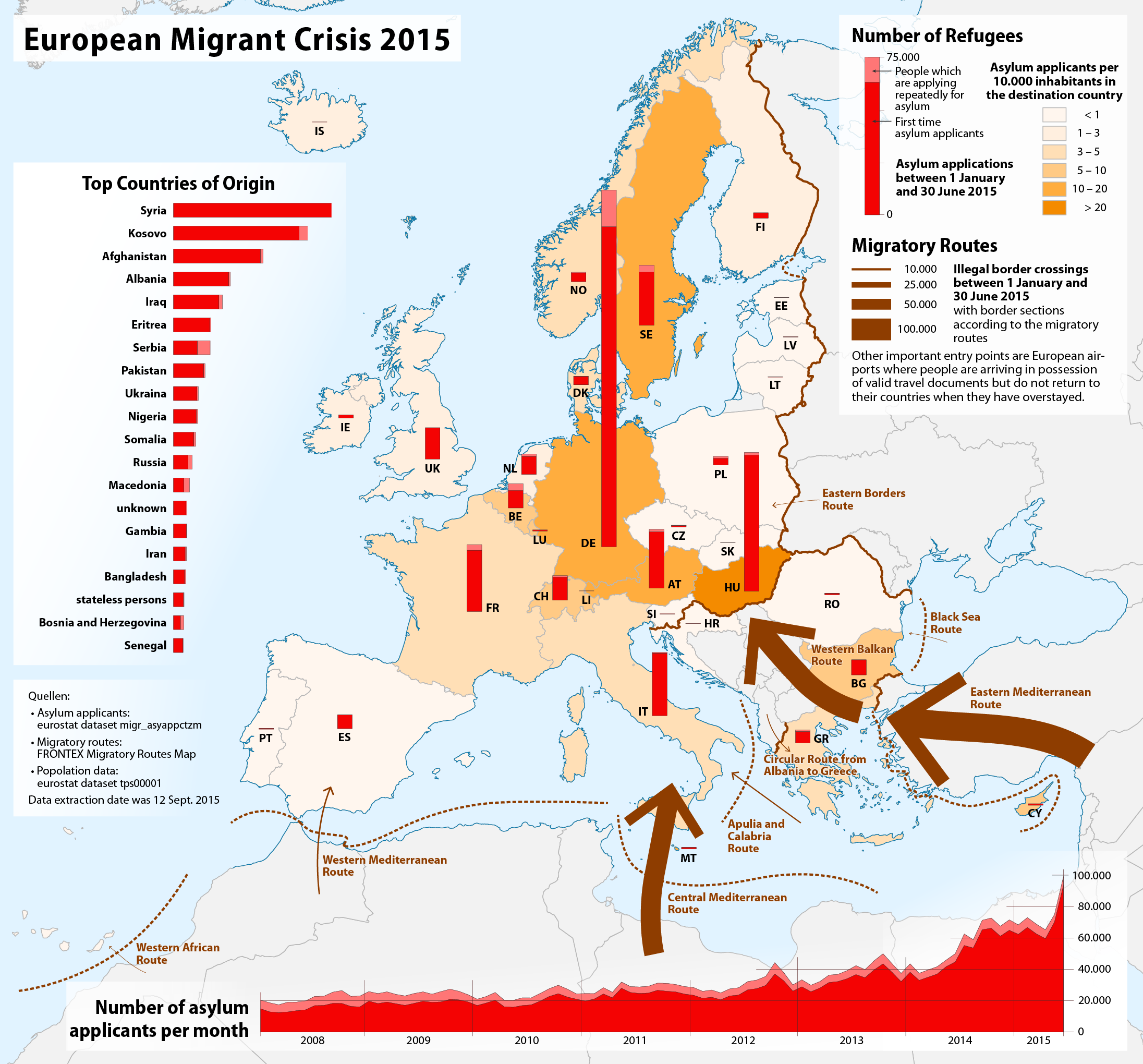
Image: European migrant crisis. Asylum applicants in Europe between 1 January and 30 June 2015. - Maximilian Dörrbecker © Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license
Download European Migrant Crisis 2015
The Middle East
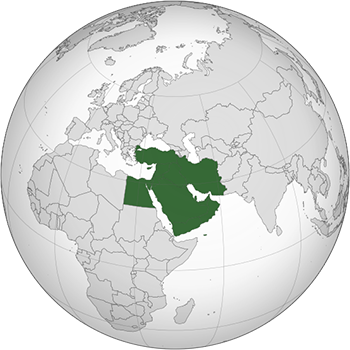
Image: Middle East - TownDown © Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license
Skill – Historical Geography
The modern history of the Middle East began at the end of World War 1.
Earlier History (in order) included:
- Over 500 years as part of the Ottoman (Turkish) Empire.
- Before this the region had been fought over by rival powers of Christianity and Islam since the 7th Century AD.
- Before the 7th Century the dominant power was the Christian Byzantine Empire.
- The Byzantine Empire was Eastern part of the Roman Empire which split up.
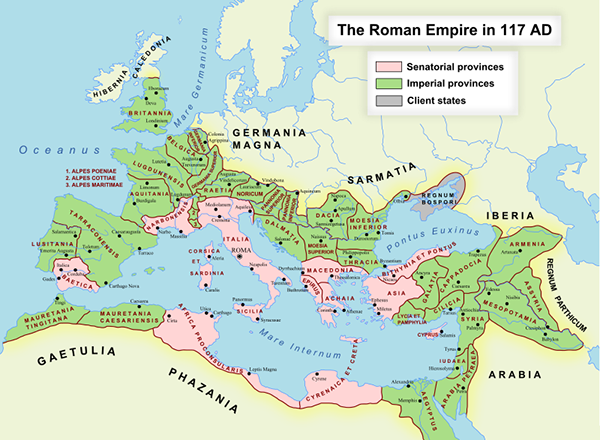
Image: The maximum extent of the Roman Empire. Superimposed on a physical map - Andrei nacu © Public Domain
- Before the Roman invasion the Middle East has often been described as ‘The Cradle of Civilisation’.
- This is because this was the region where many of the great ancient civilisations grew; these included:
- Egyptian
- Jewish
- Babylonian
- Assyrian
- Persian
- This is because this was the region where many of the great ancient civilisations grew; these included:
This is the place of many of our (human beings) most important discoveries:
- The birth of agriculture
- Use of technology/tools
- Medicine
- Architecture
- Mathematics
- Metal working
- Pottery/Ceramics.
Several of the world’s great religions including Islam, Judaism and Christianity came from this region.
Modern History
- After over 500 years as part of the Ottoman Empire things started to change quickly at the start of the 20th Century.
- Oil was discovered in 1908 and several places were invaded by Britain and France.
- In 1914 the Ottoman Empire joined with Germany and Austria/Hungary for World War 1.
- After being on the losing side the Ottoman Empire was broken up.
- Several wars soon started such as the Turkish War of Independence which led to the creation of modern Turkey in 1923.
- Most of North Africa and the Middle East came under French and British control.
- During WW 1 Britain had promised control of large areas to powerful local Arab leaders such as Sharif Hussein in return for attacking the Ottomans.
- After 1918 these promises were mostly honoured with several new countries being created.

Image: Hussein Bin Ali - Unknown Author © Public Domain
- But there was to be great disagreement in Palestine:
- Local Arab leaders believed that this area was to be part of the area controlled by Arabs
- But the British had promised this area to become a new Jewish ‘homeland’.
- After 1918 this process began:
- Palestine was split into two parts with a Jewish government in Western Palestine operating under British protection.
- World War 2 resulted in the entire region being part of the larger global conflict.
- After 1945 the region was to become very unstable with many wars:
- Wikipedia lists 69 conflicts/wars since 1946 many of which involved the new Jewish homeland Israel.

Image: Flag of Israel - Typhix © Public Domain
- On the first day of its independence in 1948 Israel was invaded by the armies of Egypt, Syria, Transjordan, Lebanon, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia.
- Almost constant conflict continued until peace deals signed in 1993.
Important Issues
- Within the region only Turkey, Israel & Lebanon became democracies with most countries becoming monarchies or dictatorships.
- In several areas there were brutal attacks on ethnic and religious groups which could be described as genocide.
- Attempts at political reforms within countries could be met with imprisonment, torture and murder.
- Religious differences could result in persecution as could sexuality which could be persecuted by state sanctioned murder.
- Eventually persecutions of populations, promotion of international terrorism, open invasions of neighbouring countries and threats to global security & oil supplies forced international military action in several locations.

Image: Gulf War photo collage for use in the infobox - User:Acdx © Public Domain
Since 1990 the region has been dominated by events in and around Iraq
Many recent & current refugees come from Iraq.
- In 1990 Iraq had the 4th largest army in the world.
- Iraq had been at war with Iran from 1980 to 1988.
- More than 1,000,000 lost their lives.

Image: Flag of Iraq - User:Hoshie © Public Domain
- Iraq was ruled by a ruthless dictator named Saddam Hussein.
- After the war with Iran he had a lot of problems within Iraq.
- He decided that the solution was to invade his oil rich neighbour Kuwait.
- He also threatened Saudi Arabia.

Image: Saddam Hussain Iran-Iraqi war 1980s - AFP/Getty-images © Public Domain
The invasion of Kuwait was complete in a little over 2 days!
However Iraq misjudged international support and was faced by a coalition of countries led by the USA and including the UK. This conflict is often called the ‘First Gulf War’.
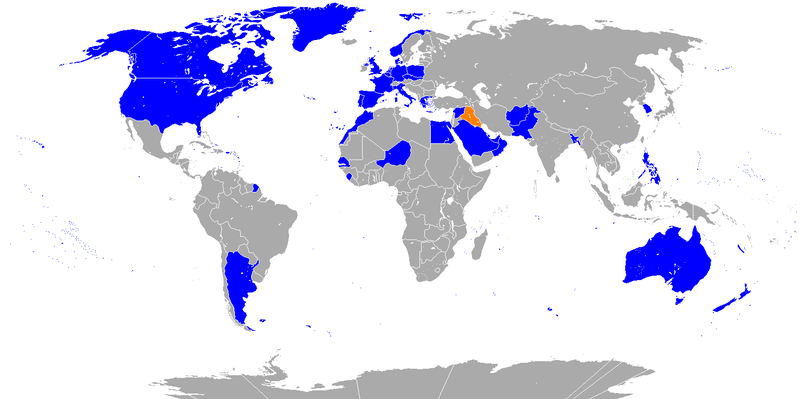
Image: Coalition of the Gulf War vs Iraq - Author Unknown © Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license
Iraq was quickly driven out of Kuwait by the coalition; 100 hours after the ground attack began it was over.
However many new problems started in Iraq:
- In 1991 as Iraq was forced out of Kuwait two main groups in Iraq rebelled; these were:
- Kurdish people in the north and
- Shia Muslims in the south.
- Kurdish and Shia groups then suffered awful persecution:
- As more than 2,000,000 refugees were fleeing Iraq they were repeatedly attacked from the air.
- In the south of Iraq several rivers were diverted to:
- cause floods in some areas and
- to deny other areas water for drinking and growing food.
- In some areas chemical weapons were used including mustard gas and sarin nerve gas.
- Many Kurdish and Shia groups were attacked using local women and children as ‘human shields’.
- In Kurdish and Shia areas Iraq condemned everyone under ‘collective responsibility’ and many were tortured, raped and burned alive.
- So far over 200 mass graves of victims have been discovered with the largest containing over 10,000 victims.
Iraq War

Image: Iraq War montage - Futuretrillionaire © CC BY-SA 2.5 / Public Domain
- In 2003 a new coalition was to invade Iraq this is often called the ‘2nd Gulf War’
- Iraq had threatened the West with ‘Weapons of Mass Destruction’. Iraq had a history of using chemical weapons.
- Iraq also had over 500 tonnes of uranium for ‘dirty’ radiation based weapons or even a nuclear bomb.
- Threats of ‘Weapons of Mass Destruction’ were one reason why many countries joined the war against Iraq.
- However there was also evidence of genocide within Iraq for which international law required action.
Victory was quick but peace has been hard to achieve with many different groups fighting coalition forces, the new Iraq Government forces and each other.
- This has often been called the Insurgency.
- Between 2003-2011 British military casualties were 179 killed and 3,598 wounded.
- One of the insurgency groups became the so called Islamic State/ISIL.
2015 Control of Iraq & Syria
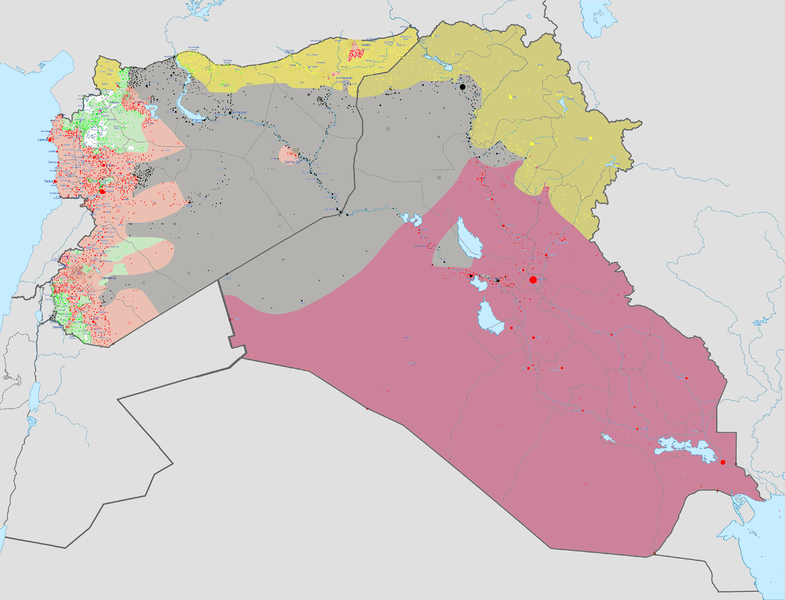
Image: Syria and Iraq 2014-onward War map - Haghal Jagul © Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication

- Between 2003 and 2006 there were probably over 600,000 violent deaths.
- This was over 500 people per day.
- Today a brutal war between so called Islamic State/ISIL, Iraqi Government forces and Kurdish forces has resulted in:
- genocides of minorities such as the Yazidis as well as widespread:
- enslavement
- torture
- rape
- murder.
- genocides of minorities such as the Yazidis as well as widespread:
- In many areas basic things like power, water and even a food supply have stopped.
As a result of all of this Iraq is a big source of.
Pupil Activity
- Imagine that you are an Iraqi refugee in Europe.
- You are being interviewed by the BBC.
Say why you left Iraq.
Use a list of bullet points.
Teacher Box
The resource is designed to be used as whole class resource from the front of the classroom on the projector/interactive whiteboard.
The various graphics should be supported by teacher exposition based on the text which will not be readable in permitted time to the vast majority of pupils), following this it is ideal that the students have access to the online resource in order to work on the activity sheet (designed to be printed on A3 size paper).
Ideally these activities will be supported by the use of a network room, tablets/laptops or students own phones/devices if permitted.
However the activities are also designed to be used in a typical one hour lesson with the teacher input using the resource from the front of the classroom alongside the resource sheet.
Students can then be set a homework task to study the three articles in advance of the following lesson.
The resource and accompanying sheet is designed to support the LNF framework while giving students key geographical knowledge about places in relation to the crisis of forced displacement from the Middle East.
Pupil Box
Either in class or at home read and complete the activities in the online resource article and in the linked articles in this edition of Geography in the News. Attempt to complete all of the activities in the resource sheet.
What you will learn:
- You will increase your knowledge issues in the Middle East
- You will increase your understanding of how these factors may affect human beings and human activities
- You will have you the opportunity to learn or practice important literacy and numeracy skills.
You will learn new geographical terms highlighted in purple these should be learned and added to a glossary. A glossary is a list of words and their meanings. You could have one in the back of your geography exercise book, if you have a planner it is probably a good place to keep a glossary, or you may keep a separate glossary or word book. A good glossary helps you build your vocabulary and your literacy. Research meanings using related article content, discussion or a dictionary (either online or a book).
Other articles you may find of interest, Mexico to USA migration, Migration in the UK and Making Decisions - The Migrant Crisis.