Plate Tectonics Overview
Plate Tectonic Model Overview
In the main article we finished off by looking at this map.
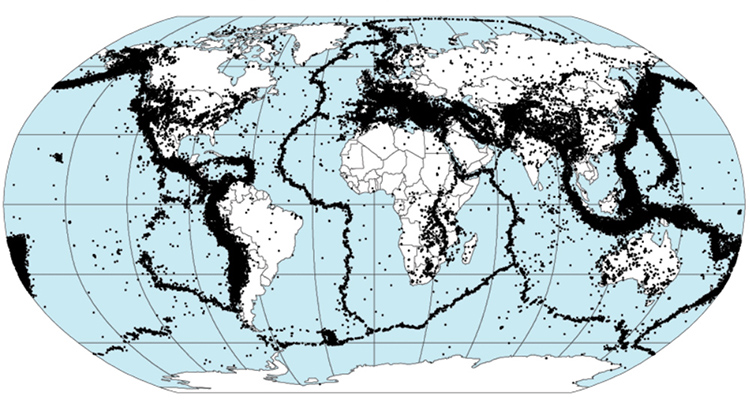
Image: Quake epicenters 1963-98 - NASA, DTAM project team © Public Domain
Using maps like these of earthquakes and volcanoes helped scientists to develop a model to help explain what is happening.
This model is called the Plate Tectonic Model.
The model divides the cooler hard upper layers of the earth into pieces called tectonic plates.
Over time these move and this helps to explain where most of the earthquakes and volcanoes occur.
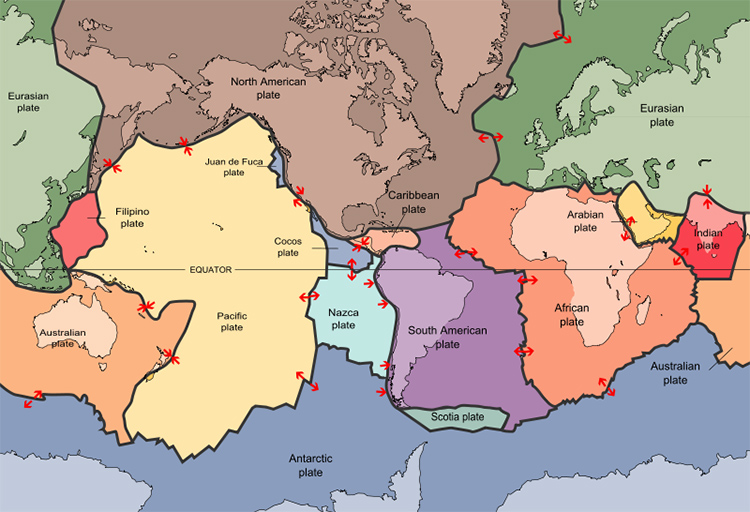
Image: Plates tect2 en - USGS © Public Domain
The main tectonic plates can be seen on the map above like pieces of a jigsaw.
Danger Volcano! KS2 Link - Click below
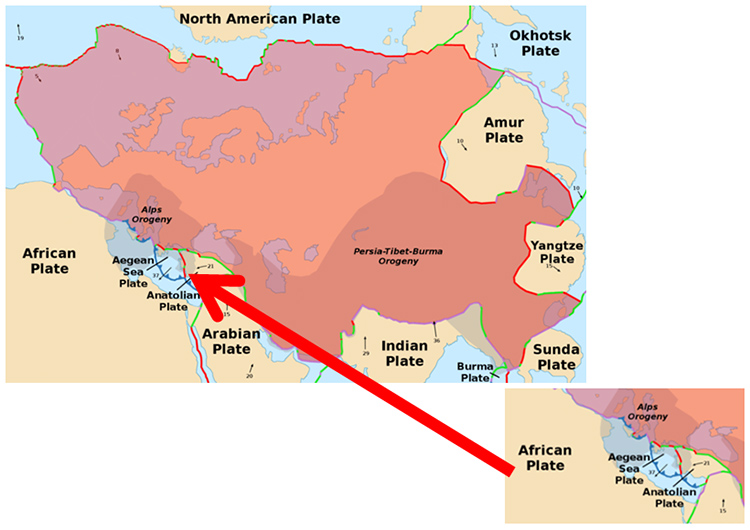
Italy & the surrounding tectonic plates
Image: EurasianPlate - Alataristarion © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International
The African Plate is moving Northwards into the Eurasian Plate
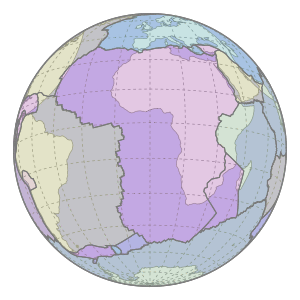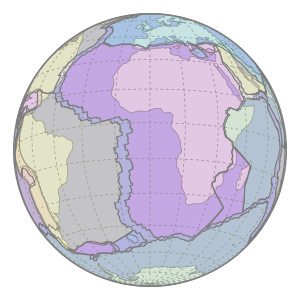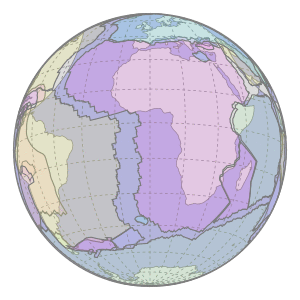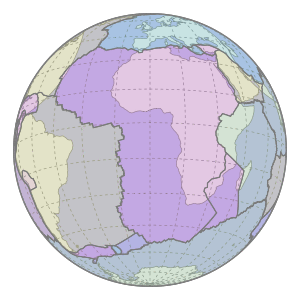
Image: Motion of Nubia Plate - Rollingfrenzy © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International
Italy is sandwiched between the main huge African Plate and the large Eurasian Plate.
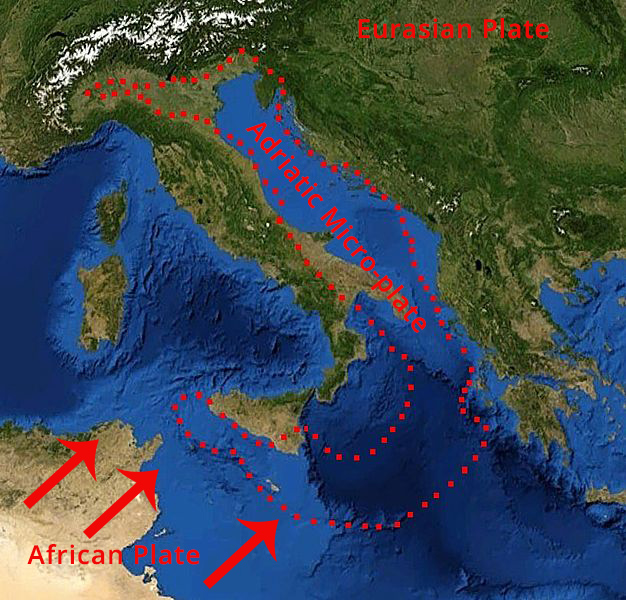
Image: Adriatic Plate - Eric Gaba (Sting) / NASA © Public Domain
The Tectonic Plates have been moving for millions of years since a giant ‘super-continent’ called Pangaea started breaking up 200-180 million years ago.
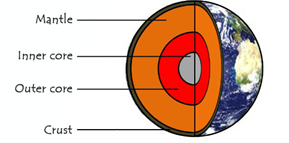
The tectonic plates are made up of cooler rigid rocks of the crust and upper mantle.
Below this the lower mantle rocks are hot enough that they can flow.
Try to think of these two layers as toffee:
- The hard layer is like a toffee in the fridge - hard enough to break your teeth.
- The soft layer is like a toffee that you put somewhere warm for a few hours like a trouser pocket.
The centre of the Earth is very hot and this heat moves outwards to the surface; one way that it does this is in giant convection (warm things rise and cooler things sink) currents in the softer mantle rocks.
These currents in the mantle pull the Tectonic Plates above them.
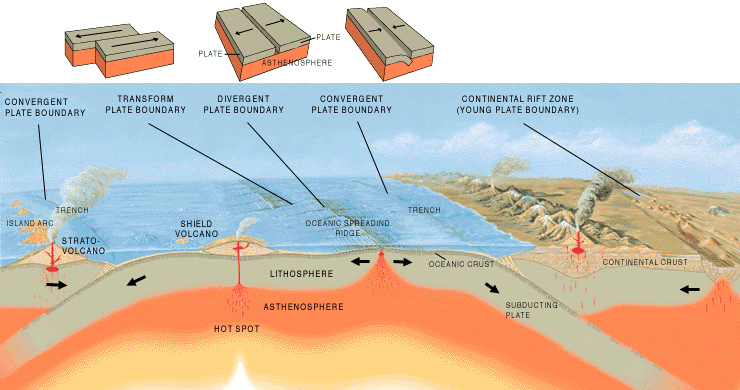
Where they meet we have different types of boundaries and these lead to different types of volcanoes, earthquakes and landforms.
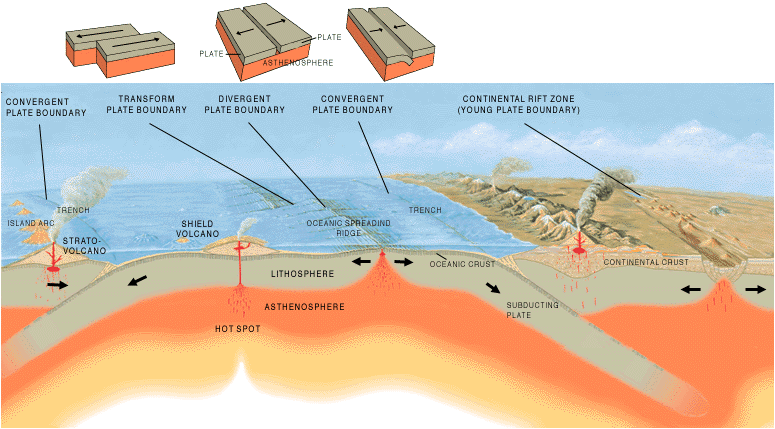
Image: Tectonic plate boundaries - Jose F. Vigil. USGS © Public Domain
Pupil Activity
Use a mind map type of diagram to show the main points of the Plate Tectonics Model.