Investigating What Causes Climate Change
In this linked article we are going to look at what causes climate change.
- It is always a good idea to make sure that we understand key terms such as climate.
- People often get confused between the terms weather and climate.
- Weather is the conditions of the air at a moment in time.

Image: Rain-on-Thassos - Edal Anton Lefterov © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported / GNU Free Documentation License
You can see the weather just by looking outside of the window; is the air moving along the surface? If it is we call this wind.
- Are there clouds (condensed water) in the air?
- Is there water moving from the air to the surface? We call this precipitation and it includes rain, drizzle, snow, sleet, fog, mist, dew, frost and rime.

Image: High Desert Fog - Jessie Eastland © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
- If the sky is not covered in clouds then depending on the time of day the sun could be shining.
- You could take a thermometer outside and find out the temperature.
Climate is the average of the weather conditions over a period of time (usually 30 years).
Now that we know what climate is we can discuss what is meant by climate change?
Climate change happens all of the time and is natural; weather and climate are almost never the same so there are always slight changes in climate.
The big meeting in Paris and the historic agreement however is about climate change caused by human activity.
Climate change is the term now used though in the past ‘global warming’ has been used as well as the term the ‘greenhouse effect’.
- Global warming is not really an accurate term as not everywhere on the planet is predicted to actually get warmer.
- The greenhouse effect is also a poor use of a term because it is natural and happens without human beings.
- Certain gasses in the atmosphere trap heat.
- These gasses act like the glass of a greenhouse keeping our planet warmer than it would otherwise be.
- Scientists have calculated that without the natural greenhouse effect Planet Earth would be approximately 32°C colder.

Image: Eden project - A1personage © Wikimedia Commons - Public Domain
Anthropogenic Climate Change
Human activities which affect and change the climate can be looked at in two main ways:
- Emissions
- Sinks
We have already talked about the natural ‘greenhouse effect’; certain naturally occurring gasses such as Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4) and water vapour (H2O) have the ability to absorb heat that would otherwise escape in to outer space.
As a result these ‘greenhouse gasses’ cause the greenhouse effect which naturally keeps us around 32°C warmer than we would otherwise be.
Emissions
This is where we add gasses to the atmosphere.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
CO2 is added when we burn fossil fuels such as coal, gas and oil. Carbon from ancient times (hundreds of millions of years ago) was locked away underground when living things became buried.
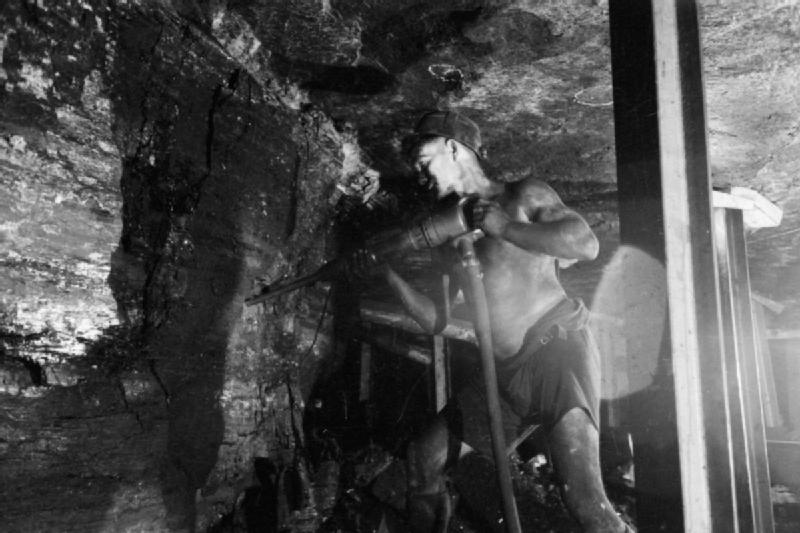

Image: Men of the Mine- Life at the Coal Face, Britain, 1942 D8263 - Ministry of Information Photo Division Photographer © Wikimedia Commons - Public Domain
Coal, oil and gas are known as fossil fuels. When we burn them in our homes, power stations and petrol/diesel (petrol and diesel are made from oil) engines the Carbon from the fuel joins with Oxygen from the air to make CO2.
The relationship between temperature and CO2 can be seen in these graphs showing both of these over the past 450,000 years. This information has come from drilling deep ice cores.
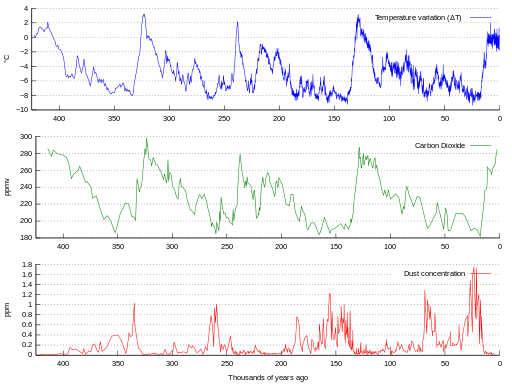
Image: Vostok Petit data - NOAA © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported / GNU Free Documentation License
Methane (CH4)
Methane or CH4 comes from a range of human activities:
- Waste products such as sewerage and food waste decompose and produce methane.
- Animals especially farm animals are a big source.
- Flooded areas produce methane and rice is produced in flooded fields. Rice growing is another big source.

Image: Biodegradable waste - Muu-karhu © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported / GNU Free Documentation License
Sinks
Sinks are traps for greenhouse gasses. An obvious sink is the forests of the world as trees absorb CO2 and lock it up in their trunks, roots and branches.

Image: Lacanja burn - Jami Dwyer © Wikimedia Commons - Public Domain
The fossil fuels such as coal gas and oil are ancient sinks which we are digging up and releasing back into the atmosphere.
A big sink for Methane is in the frozen soils of the Arctic. These soils are called the permafrost and sadly as temperatures increase in the Arctic the permafrost is melting more and more each year.
Melting Permafrost on the Beaufort Sea

Image: Beaufort Permafrost1 - Awing88 © Wikimedia Commons under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
Pupil Activity
Draw up a table headed Emissions and Sinks; under each heading make a brief note of how YOUR day so far has had an effect on BOTH.

