Why Is The Risk Of Coastal Flooding Increasing?
Erosion
On coastlines erosion is subdivided into four main types:
- Hydraulic Action
- Corrasion (Abrasion)
- Attrition
- Solution (Corrosion)
Hydraulic Action
Hydraulic action is the force of water; as well as the impact of simply being hit by waves this also includes the effects of trapped pockets of air.
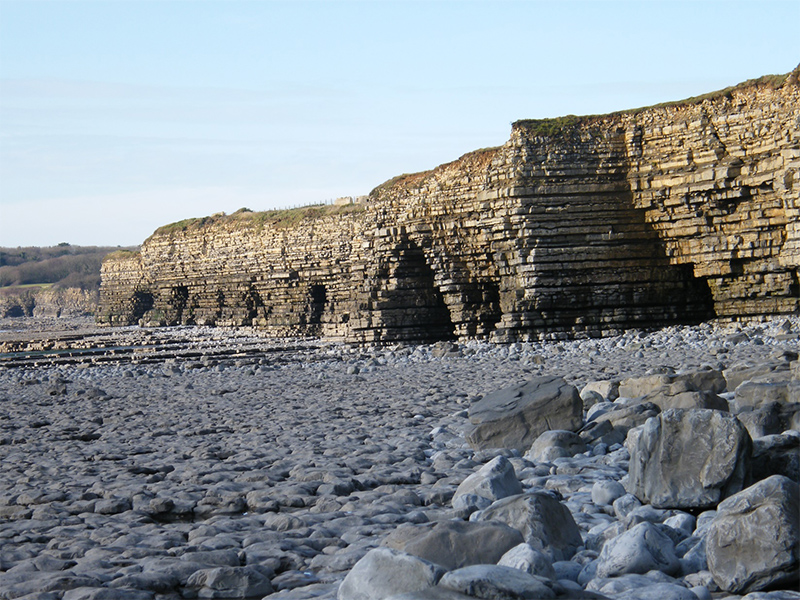

As well as the power of the wave itself a breaking wave will often curl over trapping a pocket of air.
Even if it does not do this then it may strike a cliff face with a crack or small cave. The pockets of air are compressed or squeezed by the wave creating high pressure (such as blowing up a balloon) which is then released suddenly (such as popping the balloon).
This pressure change on its own can shatter rock, but repeat it hundreds of times as wave after wave hits and even the strongest rock can be blown apart.
- Cracks become small caves which become larger caves. These can work their way deep into the rock following cracks.
- In headlands (rocky areas sticking out into the sea) these caves can join up from each side and form arches.
- Eventually the roof of an arch may collapse leaving an isolated pillar of rock called a stack.
Corrasion
Corrasion is the name for erosion in which the water or waves uses rocks and stones as tools to increase erosion; sometimes the term abrasion is also used to mean the same thing.
Corrasion/abrasion from rocks and stones carried by waves is added to the hydraulic actions of the waves as they further hit the shore line.

This is often seen as a notch at the base of cliffs as they are undermined by the sea which can cause them to collapse.
In the pictures you can see such notches along the Glamorgan Coastline and attempts to fill them in with bricks and cement to protect an important clifftop lighthouse.

Attrition
Attrition is where the rocks and stones moved by waves and water are broken up, rounded and smoothed.
Corrosion
Corrosion is the name for erosion in which the water or waves chemically dissolves rocks and stones; sometimes the term solution is also used to mean the same thing. Some types of rocks such as limestone can dissolve if there is acid in the water. Just like sugar dissolves in warm water.
Transportation
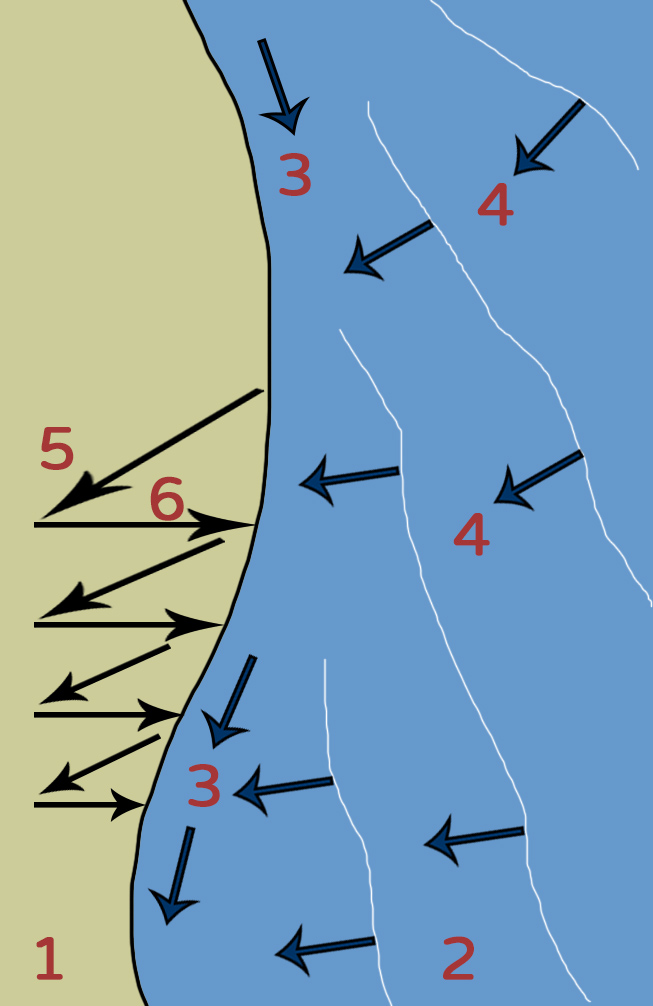
The most important process of transportation is caused by longshore drift.
- Longshore drift is caused when waves hit the shoreline at an angle.
- This is caused by the direction of the wind.
- The most common wind direction is called the prevailing wind direction.
- This usually sets up the direction of longshore drift.
- As the waves hit the beach at an angle the swash moves material up the beach at this angle.
- The backwash usually moves material straight back down the beach due to gravity.
- Through this process material moves in a zigzag pattern along a beach.
Deposition
Eventually the material which has been eroded and transported will be deposited.
The transported material may move into a more sheltered part of the coastline where it may start to be deposited as a beach.
Places with stronger waves especially those facing a long fetch a beach will normally be a very flat sand beach backed by a bank of large cobble stones.
This type of beach is called a storm beach and Newgale is a very good example.
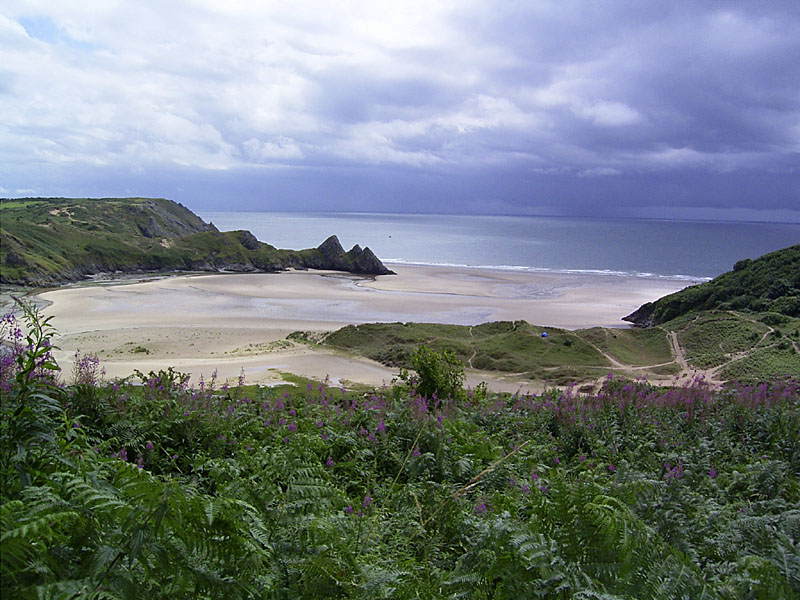

Lower energy sheltered beaches will tend to have a slightly higher angle/profile of sand and will often be backed by sand dunes.
This can be seen in this photograph of Three Cliffs Bay on the Gower Peninsular.
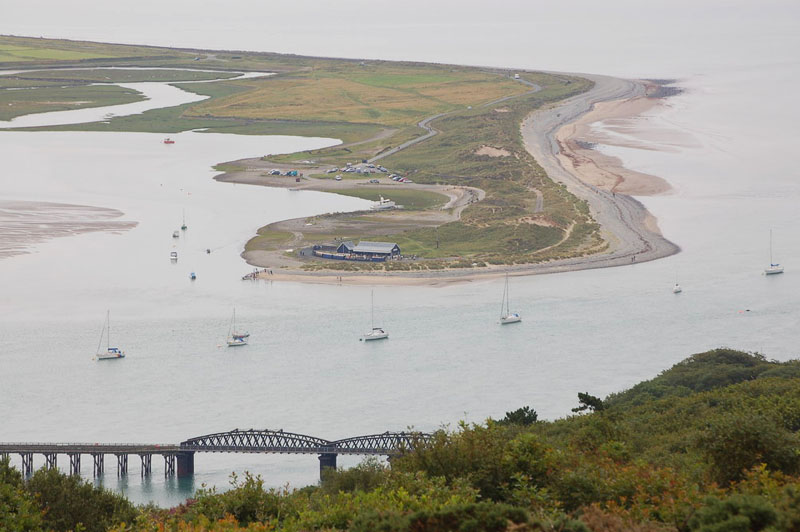

Photo from Wikipedia by Author; Roger Davis used under CC BY
Sometimes longshore drift will carry on when a beach reaches a place where the coastline changes direction.
When this happens the longshore drift will drop its sandy load into the water and a strange beach will grow out into the sea surrounded on three sides by water.
This type of beach is called a spit; they are quite common in Wales. This example is Fairbourne Spit also known as Penrhyn Point in Gwynedd which is located at the mouth of the River Mawddach where it reaches Cardigan Bay.
Pupil Activity
After taking the quiz you should be ready to attempt the geographical enquiry. Make sure that you use the geographical terms that you have learned.

