Demographic Change
Population means the total number of people living in a particular location (however we can also look at populations other than humans such a particular species of bird in a National Park). To understand population we need to look at the impacts of births, deaths and migration.
Births are usually measured using the birth rate. This is the number of live births per year per 1000 of the total population it is usually written as births/00 - such as 90/00 this is different to percentage (or per 100 which is written as %).
Deaths are usually measured using the death rate. This is the number of deaths per year per 1000 of the total population again it is usually written as deaths/00 - such as 9 0/00.
The difference between birth and deaths is called Natural Increase; it is calculated by subtracting the death rate from the birth rate. Even if there is no increase it is still called Natural Increase but is written as a minus number (such as -0.5) usually per 1000 of the population.
Population Density
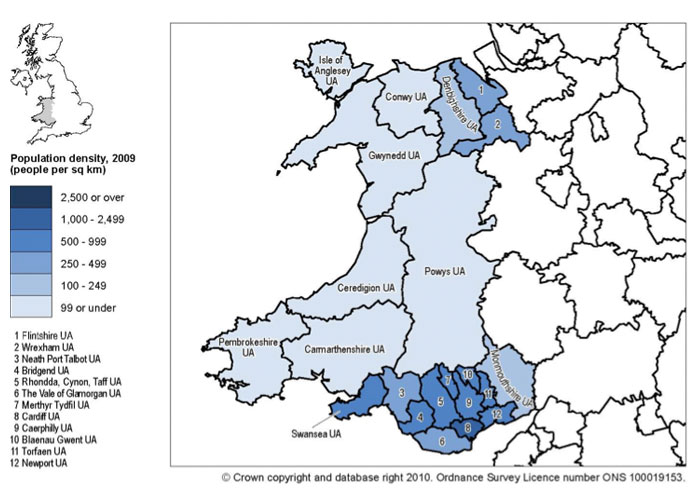
Looks at the number of people living in an area. Usually it is worked out by dividing the total population by the area in km2.
Population density does not tell us if an area has too many people. Areas with a low population density are sometimes described as being sparsely populated; however they may still have too many people.

Sparse Population
Geographers look at the number of people in an area and the quality of life for those people and impacts on the environment. The number of people which would give the best quality of life together with sustainable use of the environment is termed optimum population. If there are more people it is called over population and if there are less it is called under populated. Unemployment is a clear sign of overpopulation and many areas in Wales with low population densities have high unemployment, especially through the winter when there is less work in agriculture and tourism.
Migration is the movement of people from one place to another. When we use the term in regards to population we are looking at long-term (at least 6 months but usually several years) or permanent movements.
There are a number of ways of classifying migration:
Compulsory or forced migration occurs when people have no choice about moving.
-
Forced migrants who move to another country are called refugees.
-
Physical reasons such as earthquakes, floods or droughts.
-
Human reasons such as war or persecution.
Voluntary migration is when the migrant makes a decision to move.
When someone migrates there will be both push and pull factors involved.
Push factors are the bad things about where a migrant lives. There may be no work, few services and a low standard of living.

Push Factors
Pull factors are the good things about the place they are moving to. The location may be nearer to relatives, offer a better education or have a better climate.

Pull Factors
Globally the largest type of migration is urbanisation. This where people move from rural areas to urban areas. This is a massive process in LEDC's but is also important in MEDC's such as Wales where people migrate from rural parts of Wales such as Powys to urban areas such as Cardiff.
For more information on international migration visit the 'Welsh Ethnicity' article.
Related links
Pupil Activity
After taking the quiz you should be ready to attempt the Decision Making Exercise presentation. Make sure that you use the geographical terms that you have learned.


