Issues in the C.B.D.
Welcome to the C.B.D.
The C.B.D. or Central Business District is an area within a large town or city where certain types of businesses group together. It includes the High Street and shops, but also covers financial services like banks.
 When we say banks, we don’t mean the branches where you might go to pay in some money or go to a cash machine. These are the big offices where bankers decide how to invest large amounts of money. Other large businesses such as insurance companies can also be found here.
When we say banks, we don’t mean the branches where you might go to pay in some money or go to a cash machine. These are the big offices where bankers decide how to invest large amounts of money. Other large businesses such as insurance companies can also be found here.
The C.B.D. usually grew around the place where transport routes like roads and railways came together. We call these transport nodes. They were the place where small trading businesses provided goods for travellers and people working close by. Retailing (selling goods and services to the public) grew out of these small businesses to become the kinds of High Streets we see today.

In some centres, like Cardiff, the businesses continued to grow. Because they were surrounded by the town they could not grow outward so they grew upward instead. More importantly, rents on land or taxes were often paid by land area so it made good business sense to build upwards.
This is why some parts of towns and cities have such high buildings. You should be able to spot the C.B.D. of a large town or city by looking at the heights of buildings. Usually, the closer you get to the C.B.D., the more floors the buildings have. You could try using Google Maps or Google Earth (what we call Geographical Information Systems or G.I.S.) to see if this is true.
Challenges facing the Central Business District - The growth of 'out of town' locations
 One of the biggest challenges to a C.B.D. is the growth of out of town business parks and shopping centres. Because more people than ever own cars many shoppers want an easy drive and lots of parking when they go shopping. This has led to the growth of out of town retail parks like Parc Trostre at the edge of Llanelli.
One of the biggest challenges to a C.B.D. is the growth of out of town business parks and shopping centres. Because more people than ever own cars many shoppers want an easy drive and lots of parking when they go shopping. This has led to the growth of out of town retail parks like Parc Trostre at the edge of Llanelli.
Here's a question for you...
With so many large, well known ‘flagship' stores moving to retail parks, how can town centres continue to draw in shoppers?

In the past, the number of workers and customers from non-retail businesses in the C.B.D. would have kept the big flagship stores in the town centre. However, the ‘out of town’ parks have also attracted businesses other than shops (banks, insurance companies and so on). This photograph shows the Celtic Lakes Business Park on the edge of Newport which is pulling away many businesses that would traditionally be in the C.B.D.
Without this footfall major retailers have deserted the city centre. Without the attractions of major retailers in the C.B.D. other businesses also move out of town; it becomes a vicious cycle or what is sometimes called the domino effect – one business leaves which pushes the next which then pushes the next and so on.
Challenges facing the Central Business District - Maintaining the shopping experience
Recently geographers have started using a new phrase – ‘clone towns’. A clone town has lost its individual character or identity and is very similar to lots of other towns. They all end up with the same chain stores in the same sort of spaces in the C.B.D. Over the last 10-20 years smaller, local shops have been driven out by national and international chains until there is a lot less choice for shoppers.
 The problem is that there is so much competition from out of town shopping centres and business parks that clone towns may not be able to attract enough shoppers. The size of the area that people come from to visit a shopping centre is called its ‘sphere of influence’. The size of its sphere of influence will determine the number of shoppers and other visitors that are needed to keep businesses in the C.B.D. going.
The problem is that there is so much competition from out of town shopping centres and business parks that clone towns may not be able to attract enough shoppers. The size of the area that people come from to visit a shopping centre is called its ‘sphere of influence’. The size of its sphere of influence will determine the number of shoppers and other visitors that are needed to keep businesses in the C.B.D. going.
This number of visitors is called the threshold population and it will affect the range of goods and services on offer in the C.P.D. (for example, shops selling large, expensive items like televisions need a lot of potential customers in order to stay in business, so their threshold population is large).
Concept: The Sphere of Influence
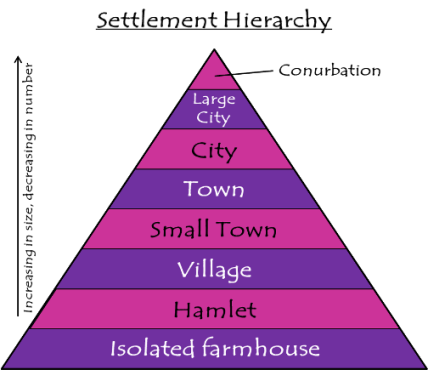 The sphere of influence is the area that a settlement provides goods and services for. It is based, in part, on the idea of 'Settlement Hierarchy’.
The sphere of influence is the area that a settlement provides goods and services for. It is based, in part, on the idea of 'Settlement Hierarchy’.
If you look at the pyramid diagram, it shows that there are lots of smaller settlements such as isolated buildings or groups of houses called hamlets. As settlements get bigger and become villages or small towns there are less of them.
Once a village has a sphere of influence covering several hamlets it may reach the threshold population required to support a small shop, post office or pub.
When settlements get larger they reduce in numbers again because they need a very large threshold population to support all the different goods and services. At the very top of the settlement hierarchy there may be just one large city.
Sometimes towns and cities grow or join together to create areas called a conurbation. A conurbation is starting to develop along the M4 motorway in South Wales as Cardiff begins to merge with other towns and cities such as Newport.
Brain box...
A settlement’s place in the settlement hierarchy and its sphere of influence controls the range of goods and services that it can sustain. Small settlements may only sell low order (cheaper) goods that people need all the time like milk or bread. Large cities will have a full range of expensive high order goods and services that people only buy very rarely.
Until recently this would have included large electronic goods like TVs or computers, but most of these types of retailers moved out of town or onto the internet.
Some out of town retail parks have been placed carefully to try to attract visitors from several town centres. A good example is Talbot Green in Llantrisant which is on the edge of the sphere of influence of much of Cardiff, Bridgend and Pontypridd.
Challenges facing the Central Business District - The rise of 'New Retailing'
The photograph below shows the inside of the giant internet retailer Amazon’s warehouse near Swansea. Online shopping is a real competition for many C.B.D. retailers, although it affects some shops more than others.

Digital media like music or movies can be downloaded from the internet and many shoppers do not want to fill their homes with plastic boxes of DVDs or CDs. Music and DVD retailers have to adapt quickly or die. However online shopping still only accounts for around 10% of UK purchases. The bigger challenge comes from the rise of super retailers.
Amazon's warehouse, Swansea
Brain box...
Until recently a supermarket was somewhere that a shopper went to buy food. Now some companies want to make your supermarket a one-stop shop with electronics, home ware, clothes and even services such as opticians and pharmacies
People say that “time is money”, and many shoppers like the speed and convenience of having everything they need under one roof. Often these super retailers can split their staff between several different sections of the store. They can also buy large amounts of their products in one go which saves the company money. We call these economies of scale and as a result they can charge less than shops in the C.B.D.
Many supermarkets have even added online shopping to their services which makes it easy for their customers to quickly collect their shopping at a convenient time, or even have it delivered, often on the same day that they placed the order.
Lots of people would say that they provide best of all worlds which is why they have often built up such large shares of the market.
Pupil Activity
Use a G.I.S. (Geographical Information System, e.g. Google Earth or Google Maps) to investigate the range of goods and services in settlements of different sizes. Complete a tally chart to see how many of the following are in each settlement town centre.
-
Low order goods
-
High order goods
-
Low order services
-
High order services
-
Leisure
-
Vacant
Draw graphs for each settlement and decide whether the ideas of sphere of influence/threshold populations and settlement hierarchies are still true.

